Why do we use nutrient agar jelly to grow our samples on
Answers
Answer:
To give the bacteria the opportunity to cultivate.
Explanation:
If you really think about it, us humans eat because we extract the energy from food to power our cellular reactions. Assuming you mean for bacteria, they are like us in the sense that they need nutrients so their systems can keep running (metabolism - the sum of all chemical reactions in a specimen). We give them what they need so they can grow, much like how we need to eat food to grow. We do this so they can proliferate. Then we can study them once there are enough. The agar is really just to provide a semi-solid medium to keep the bacteria samples suspended at the top. If it was liquid they would sink down to the bottom, and then you couldn't interact with them as easy. You can also think of it as a solid surface for them to grow on so they can grow in colonies. Hope this helps.
Related Questions
Question 1: Draw a voltaic cell and identify its components then write cell notation: a. 2Ag+(aq) + Pb(s) →→→ Pb²+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Answers
Answer:
sorry i apologize that for my ability it's difficult to provide a diagram but your diagram will expressed as follow. also in summary it represented through notation. below
For the given reaction:
2Ag⁺(aq) + Pb(s) → Pb²⁺(aq) + 2Ag(s)
The voltaic cell consists of the following components:
Anode: The electrode where oxidation occurs. In this case, the anode is the solid lead (Pb) electrode.
Cathode: The electrode where reduction occurs. In this case, the cathode is the solid silver (Ag) electrode.
Anode electrolyte: The electrolyte solution surrounding the anode. It contains silver ions (Ag⁺(aq)).
Cathode electrolyte: The electrolyte solution surrounding the cathode. It contains lead ions (Pb²⁺(aq)).
Salt bridge: A tube or pathway containing an electrolyte solution that connects the two electrolyte solutions, allowing ion flow and maintaining electrical neutrality.
Now, let's write the cell notation for the given reaction:
Anode: Pb(s) | Pb²⁺(aq)
Cathode: 2Ag⁺(aq) | Ag(s)
The cell notation represents the two half-cells separated by a vertical line. The anode is written on the left, and the cathode is written on the right. The single vertical line represents the phase boundary between the electrode and the electrolyte solution. The double line represents the salt bridge.
Therefore, the cell notation for the given reaction is:
Pb(s) | Pb²⁺(aq) || 2Ag⁺(aq) | Ag(s)
what should be considered when determining how hazardous a chemical is
Answers
When determining how hazardous a chemical is, several factors should be considered. Here are some key considerations:Toxicity, Health Effects ,Physical Properties, Exposure Routes ,Hazard Communication , Regulatory Classifications ,Risk Assessment, Environmental Impact
1. Toxicity: Assess the toxicity of the chemical, including its potential to cause harm to humans, animals, and the environment. This includes evaluating acute toxicity (short-term exposure) and chronic toxicity (long-term exposure).
2. Health Effects: Determine the specific health effects associated with the chemical, such as carcinogenicity (cancer-causing potential), mutagenicity (ability to cause genetic mutations), teratogenicity (ability to cause birth defects), and organ toxicity.
3. Physical Properties: Consider the physical properties of the chemical, including its flammability, explosiveness, reactivity, volatility, and corrosiveness. These properties can contribute to the potential for accidents, fires, or releases of hazardous substances.
4. Exposure Routes: Evaluate the different routes of exposure to the chemical, such as inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. Assess the likelihood and duration of exposure in occupational settings, consumer products, or environmental scenarios.
5. Hazard Communication: Consider the information provided in safety data sheets (SDS) and labels. Hazard symbols, risk phrases, and precautionary measures provide important information about the potential hazards associated with the chemical.
6. Regulatory Classifications: Review the regulatory classifications of the chemical, such as those provided by organizations like the United Nations (UN) Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and other regulatory agencies.
7. Risk Assessment: Conduct a risk assessment to determine the level of risk associated with the chemical's use or exposure. This involves considering factors such as the concentration or dose of the chemical, duration of exposure, and potential routes of exposure.
8. Environmental Impact: Assess the potential environmental impact of the chemical, including its persistence, bioaccumulation potential, and effects on ecosystems, wildlife, and natural resources.
It's important to note that determining the hazards of a chemical should be done by qualified professionals and may require expert knowledge, testing, and analysis. Regulatory requirements and guidelines may vary between countries and regions, so compliance with relevant regulations and standards is essential.
To know more about Toxicity refer here
https://brainly.com/question/31834789#
#SPJ11
what was found in the trap of the miller–urey apparatus that supports a hypothesis for the beginning of early life?
Answers
Miller -Urey experiments was an investigation for the components that made life on earth. The experiment used water, methane gas, ammonia and hydrogen gas. These compounds were cooled settled on the trap where they formed macromolecules latter called amino acids.
What was Miller-Urey experiment?The Miller-Urey experiment was carried out to gather data pertaining to the topic of how life first developed on Earth. The experiment used a device with a number of flasks and tubes that pumped materials that were said to be part of the initial or early atmosphere of Earth.
The methane, ammonia, and hydrogen gases were all added to a glass flask that held 5 liters and was connected in two directions to a system of tubes that also held a 500 milliliter flask that contained some water In this flask, electrodes produced electrical sparks to a mixture of gases and water vapor in order to mimic the lighting in the Earth's early atmosphere.
The cooling process results in a mixture of hydrogen, ammonia, methane, and water vapor. All the components finally settled into the trap at the bottom of the system and they are found to form macromolecules.
To find more on Miller-Urey experiments, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/18271656
#SPJ1
1. In a Stock system name such as iron(III) sulfate, the Roman numeral tells us (a) how many atoms of Fe are in one formula unit. (b) how many sulfate ions can be attached to the iron atom. (c) the charge on each Fe ion. (d) the total positive charge of the formula unit. 2. Changing a subscript in a correctly written chemical formula (a) changes the number of moles represented by the formula. (b) changes the charges on the other ions in the compound. (c) changes the formula so that it no longer represents the compound it previously represented. (d) has no effect on the formula.
Answers
Answer:
See explanation
Explanation:
1) The formula of the compound is Fe2(SO4)3. There are two ion atoms in any formula unit as we can see here. Three sulphate ions are attached to iron. Each iron ion carries a +3 charge as we saw in the formula. The total positive charge in each formula unit is +6.
Changing a subscript in a correctly written chemical formula changes the formula so that it no longer represents the compound it previously represented. Hence FeSO4 is a different compound from Fe2(SO4)3.
describe the location of the electron in Thomson's model of the atom
Answers
Answer:
In Thomson's model, the atom is composed of electrons surrounded by a soup of positive charge to balance the electrons' negative charges, like negatively charged “plums” surrounded by positively charged “pudding”. The 1904 Thomson model was disproved by Hans Geiger's and Ernest Marsden's 1909 gold foil experiment.
hich of the following bonds would be most susceptible to radical formation?
Answers
The bonds that are most susceptible to radical formation are those with weak bond energies, such as single bonds and pi bonds. Double and triple bonds have higher bond energies and are therefore less likely to undergo radical formation.
Let us discuss this in detail.
1. Bonds: Bonds refer to the connections between atoms in a molecule. They can be covalent (sharing electrons), ionic (transferring electrons), or metallic (a sea of electrons).
2. Susceptible: Susceptibility refers to the vulnerability or likelihood of something happening. In this case, it means how likely a bond is to undergo radical formation.
3. Radical formation: A radical is an atom, molecule, or ion with an unpaired electron. Radical formation occurs when a bond is broken, and each atom involved retains one of the electrons from the bond, creating two radicals.
Learn more about Radical at https://brainly.com/question/14466017
#SPJ11
Radio waves are used to transmit information on various channels. What is the wavelength of a radio wave having the frequency of 5.40 × 1010 Hz?
1. Analyze the Problem
ν = and c = Unknown: λ =
You know that because radio waves are part of the electromagnetic spectrum, their speed, frequency, and wavelength are related by the formula c = λν.
Answers
Answer:
5.56×10¯³ m
Explanation:
From the question given above, the following data were obtained:
Frequency (v) = 5.4×10¹⁰ Hz
Wavelength (λ) =?
The velocity of electromagnetic wave, frequency and wavelength are related according to the equation:
Velocity (c) = wavelength (λ) × frequency (v)
c = λv
With the above formula, the wavelength of the radio wave can be obtained as follow:
Frequency (v) = 5.4×10¹⁰ Hz
Wavelength (λ) =?
Velocity (c) = 3×10⁸ m/s
c = λv
3×10⁸ = λ × 5.4×10¹⁰
Divide both side by 5.4×10¹⁰
λ = 3×10⁸ / 5.4×10¹⁰
λ = 5.56×10¯³ m
Thus, wavelength of the radio wave is 5.56×10¯³ m
serotonin (C10H12N2O) , what is the ratio of C atoms to N atoms ?
Answers
Answer: 5:1
Explanation:
1. A student in lab measures 4.6 grams of copper for an experiment. Upon further analysis he determines that he should have measured out 4.7 grams of copper. What is his percent error?
Answers
Answer:
\(2.13\%\)
Explanation:
Quantity of copper measured by a student = 4.6 grams
Original quantity of copper = 4.7 grams
Error in measurement = Original quantity of copper - Quantity of copper measured by a student \(=4.7-4.6=0.1\) grams
To find the percent error, apply the following formula:
Percent error = (Error in measurement / Original quantity of copper) × 100
\(=\frac{0.1}{4.7}(100)=2.13\%\)
1. When old cells, which normally die, instead grow uncontrollably and
form new, abnormal cells, it is called:
A. lymphoma
B. a tumor
C. carcinoma
D. cancer
Answers
3. What type of gas do plants take in?
oxygen
carbon dioxide
Answers
Answer:
Archaeology is the study of the human past using material remains. These remains can be any objects that people created, modified, or used.
Explanation:
The half life for uranium-235 is 7.0x10 8years. a. How many half-lives did the sample go through at the end of 2.8x10 9years? b. How much of a 0.74mg sample of uranium-235 will remain after 2.8x10 9years?
Answers
Answer:
A 4 half-life
B. 0.05 mg
Explanation:
A. Determination of the number of half-lives after 2.8×10⁹ years.
From the question given above,
7×10⁸ years = 1 half life
Therefore
2.8×10⁹ years = 2.8×10⁹ years × 1 half life / 7×10⁸ years
2.8×10⁹ years = 4 half life
Thus, the sample went through 4 half-lives at the end of 2.8×10⁹ years.
B. Determination of the amount of the sample remaining after 2.8×10⁹ years.
Original amount (N₀) = 0.74 mg
half life (t½) = 7×10⁸ years
Time (t) = 2.8×10⁹ years
Amount remaining (N) =?
Next, we shall determine the rate of disintegration. This can be obtained as follow:
half life (t½) = 7×10⁸ years
Decay constant (K) =?
K = 0.693 / t½
K = 0.693 / 7×10⁸
K = 9.9×10¯¹⁰ /year
Finally, we shall determine the amount remaining as follow:
Original amount (N₀) = 0.74 mg
Time (t) = 2.8×10⁹ years
Decay constant (K) = 9.9×10¯¹⁰ /year
Amount remaining (N) =?
Log (N₀/N) = kt / 2.303
Log (0.74/N) = 9.9×10¯¹⁰×2.8×10⁹ /2.303
Log (0.74/N) = 2.772 / 2.303
Log (0.74/N) = 1.2036
Take the antilog of 1.2036
0.74/N = antilog (1.2036)
0.74 / N = 15.98
Cross multiply
0.74 = N × 15.98
Divide both side by 15.98
N = 0.74 / 15.98
N = 0.05 mg
Thus, 0.05 mg of the sample will remain after 2.8×10⁹ years
The amount of uranium sample remained after 4 cycles in \(\rm 2.8\;\times\;10^9\) years has been 0.04625 mg.
The half-life can be described as the time required by the element to reduce to its half concentration from the initial concentration.
A. The number of half-life cycles can be calculated as:
\(\rm 7.0\;\times\;10^8\) = 1 cycle
\(\rm 2.8\;\times\;10^9\) = \(\rm \dfrac{1}{\rm 7.0\;\times\;10^8}\;\times\;2.8\;\times\;10^9\)
= 4 cycles.
The number of half-life cycles after \(\rm 2.8\;\times\;10^9\) years are 4 cycles.
B. The amount of sample remained can be calculated as:
Sample remained = Initial sample \(\rm \times\;\dfrac{1}{2}^\frac{time}{Half-life}\)
Sample remained = 0.74 mg \(\rm \times\;\dfrac{1}{2}^\frac{2.8\;\times\;10^9}{7.0\;\times\;10^8}\)
Smaple remianed = 0.74 \(\rm \times\;\dfrac{1}{2}^4\)
Sample remained = 0.74 \(\times\) 0.0625 mg
Sample remained = 0.04625 mg.
The amount of uranium sample remained after 4 cycles in \(\rm 2.8\;\times\;10^9\) years has been 0.04625 mg.
For more information about the half-life, refer to the link:
https://brainly.com/question/24710827
The true structure of a resonance hybrid is the structure of the most stable resonance contributor. Equivalent resonance forms contribute equally to the overall structure of a resonance hybrid.
Answers
The true structure of a resonance hybrid is determined by the most stable resonance contributor. Equivalent resonance forms contribute equally to the overall structure of the resonance hybrid.
In a resonance hybrid, molecules or ions can have multiple resonance structures, which are different representations of electron distribution. These resonance structures are connected by double-headed arrows to indicate the delocalization of electrons. The true structure of a resonance hybrid is not any single resonance structure but a combination of all resonance contributors.
The stability of a resonance contributor depends on factors such as formal charges, electronegativity, and resonance energy. The most stable resonance contributor, also known as the major contributor, has the lowest energy and contributes the most to the overall structure of the resonance hybrid.
Equivalent resonance forms have the same energy and contribute equally to the resonance hybrid. They can be interconverted through resonance, where electrons are delocalized over multiple atoms. This delocalization of electrons enhances the stability of the system.
By considering the most stable resonance contributor and the equal contribution of equivalent resonance forms, we can determine the true structure of a resonance hybrid, which represents the actual electron distribution in the molecule or ion.
learn more about stable resonance here:
https://brainly.com/question/3522100
#SPJ11
To form the universe, galaxies, solar systems, and planets you need…
I think this because....
Someone please help me
Answers
Answer: Our solar system formed about 4.5 billion years ago from a dense cloud of interstellar gas and dust. The cloud collapsed, possibly due to the shockwave of a nearby exploding star, called a supernova. When this dust cloud collapsed, it formed a solar nebula—a spinning, swirling disk of material
Explanation:
Answer:
Explanation:
Our solar system formed about 4.5 billion years ago from a dense cloud of interstellar gas and dust. The cloud collapsed, possibly due to the shockwave of a nearby exploding star, called a supernova. When this dust cloud collapsed, it formed a solar nebula—a spinning, swirling disk of material. this is because if some get to close it could burn the planet i think.
Which of the following statements correctly describe the angular momentum quantum number, symbol L? Select all that apply.
The value of l dictates the allowed values of m The values of I can range from -n to +n. This number is related to the orientation of the orbital in space. The number of possible I values equals the value of n. The allowed values of l are determined by the value of n.
Answers
The angular momentum quantum number, symbol L, is related to the orientation of an orbital in space.
The correct statements about the angular momentum quantum number are: The value of L dictates the allowed values of the magnetic quantum number (m). The number of possible L values is determined by the value of the principal quantum number (n).
The angular momentum quantum number, L, describes the shape of an atomic orbital. It determines the allowed values of the magnetic quantum number (m) and provides information about the orientation of the orbital in space. The value of L can range from 0 to (n-1), where n is the principal quantum number.
The first correct statement is that the value of L dictates the allowed values of the magnetic quantum number (m). For each value of L, there are 2L+1 possible values of m, ranging from -L to +L.
The fourth correct statement is that the number of possible L values equals the value of n. For example, if n = 3, the possible values of L are 0, 1, and 2.
The last statement is incorrect. The allowed values of L are not determined by the value of n. Instead, the values of L are limited by the range of 0 to (n-1).
Understanding the angular momentum quantum number is important in understanding the quantum mechanical properties of atomic orbitals and their arrangement within an atom.
Learn more about angular momentum here: brainly.com/question/30656024
#SPJ11
How many milliliters of a 0.80mM ammonium hydroxide solution are required to create 2.0L of 0.30mM solution? Do not include units in the answer. Your answer should have two significant figures.
Answers
To make 2.0L of a 0.30mM solution, \(6.4 \times 10^3\) millilitres of a 0.80mM ammonium hydroxide solution are needed.
What is ammonium hydroxide?An aqueous solution containing ammonium (\(NH_4\)) and hydroxide (\(OH^-\)) ions is known as ammonium hydroxide. Because it is a strong base, it totally dissociates in aqueous solutions, resulting in an alkaline reaction.
Ammonium hydroxide is utilised in a wide range of commercial and domestic applications, including the production of cleaning agents. It can be used for cleaning, deodorising, and bleaching, among other things. It serves as a dough conditioner and an
acidity regulator in the food sector.
\(6.4 \times 10^3\)
Let x = 0.80 mM ammonium hydroxide solution in millilitres is needed.
We know that molarity (mM) = moles/L
Given:
\(M_1\) = 0.80 mM
\(M_2\) = 0.30 mM
\(V_2\) = 2.0 L
As a result, we may construct the equation shown below:
(0.80 mM)(x mL) / (1000 mL/L) = (0.30 mM)(2.0 L)
Solving for x, we get:
x = \(6.4 \times 10^3\) mL
In order to produce 2.0L of 0.30mM solution, \(6.4 \times 10^3\) mL of a 0.80mM ammonium hydroxide solution are needed.
To learn more about ammonium hydroxide, visit:
brainly.com/question/31367127
#SPJ1
An ioc occurs when what metric exceeds its normal bounds?.
Answers
An ionic bond is formed when there are more or less electrons that normal in bonding atoms.
What are Ionic bonds?An ionic bond is formed when one atoms donates electrons to another specie to form an ion pair. One atom is positively charged while the other specie is negatively charged.
Hence, an ionic bond is formed when there are more or less electrons that normal in bonding atoms.
Learn more about ionic bonds: https://brainly.com/question/14484184
how many moles of kcl are present in 50.0 ml of a 0.552 m solution?
Answers
To calculate the number of moles of KCl present in a 50.0 ml solution with a concentration of 0.552 M, we need to use the formula: moles = concentration x volume (in liters)
Therefore, there are 0.0276 moles of KCl present in a 50.0 ml solution with a concentration of 0.552 M.
To find the number of moles of KCl in a 50.0 mL solution with a concentration of 0.552 M, you'll need to use the formula:
Moles of solute = Volume of solution (in liters) × Molarity
So, there are 0.0276 moles of KCl present in 50.0 mL of a 0.552 M solution.
To learn more about KCl click here: brainly.com/question/23953654
#SPJ11
4. Consider a gas sample with a volume of 10 L at a pressure of 0. 500 atm. What volume will this gas sample occupy if the pressure is increased to 2. 00 atm? Assume that the temperature remains constant and the gas sample obeys the ideal gas law. (2pts)
quickly pls
Answers
10.0 L volume will this gas sample occupy if the pressure is increased to 2. 00 atm.
What is volume?Volume is a measure of the amount of space an object occupies. It is a three-dimensional measure, meaning that it takes into account length, width, and height. Volume is measured in cubic units, such as cubic meters (m³), cubic centimeters (cm³), cubic feet (ft³), and so on. Volume is an important concept in many scientific fields, such as chemistry, physics, and engineering.
The volume of the gas sample can be calculated using the ideal gas law equation: PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the amount of substance, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is the temperature.
Since the temperature and amount of substance remain constant, we can rearrange the equation to solve for V: V = nRT/P
Plugging in the known values, we get:
V = (n)(0.0821 atm•L/mol•K)(298 K)/(2.00 atm)
V = 10.0 L
To learn more about volume
https://brainly.com/question/25736513
#SPJ4
What happens at the transition stage?
Answers
At the transition stage, one form of matter starts getting converted into another form of matter.
Solid, liquid and gas are the three phases in which matter occur in nature. Matter is interconvertible in nature i.e it can be converted from one form to another.
Melting, freezing and evaporation are the three phases of transition.
Liquid water at low temperature freezes to form solid ice. This process is known as freezing. Whereas, liquid water when provided high temperature or heat releases vapours. This process is known as evaporation. Solid ice when brought at room temperature gets converted back into liquid water. This process is known as melting.
To know more about transition stage here
https://brainly.com/question/19983755
#SPJ4
What coefficient for O2 demonstrates the law of conservation of mass?
CH (9) + _02(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
Answers
Answer:
2
Explanation:
The coefficient for O is 2 and this is an example of a combustion reaction. With the help of the coefficient 2 infront of oxygen, this equation now demonstrates law of conservation of mass.
The coefficient for O₂ that demonstrates the law of conservation of mass is
2.
The law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created
nor destroyed but can be transformed from one form to another.
The mass of the reactant and the mass of the product should be equal.
Therefore, let's balance the equation
CH4 (g) + 0₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g)
For the equation to be balanced the masses of each molecules on both
sides will be the same .
Therefore,
CH4 (g) + 20₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g)
The coefficient of 2 for O₂ will balance the masses of oxygen on both
sides of the chemical equation.
learn more: https://brainly.com/question/9797053?referrer=searchResults
A 1.00 l solution contains 3.50×10-4 m cu(no3)2 and 1.75×10-3 m ethylenediamine (en). the kf for cu(en)22 is 1.00×1020. what is the concentration of cu2 (aq) in the solution?
Answers
The concentration of Cu2+ in the solution is 3.50×10^-4 - 1.29×10^-10 M, which is approximately equal to 3.50×10^-4 M.
The formation constant, Kf, for the complex ion Cu(en)22+ is given as 1.00×10^20. The concentrations of Cu(NO3)2 and ethylenediamine (en) are given as 3.50×10^-4 M and 1.75×10^-3 M, respectively.
The reaction that forms the complex ion can be represented as,
Cu2+ (aq) + 2en (aq) ⇌ Cu(en)22+ (aq)
Let's assume that x is the concentration of Cu2+ ion that reacts with en to form the complex. At equilibrium, the concentration of Cu(en)22+ can be expressed as (1.75×10^-3 - 2x) M (since 2 moles of en react with 1 mole of Cu2+ to form 1 mole of Cu(en)22+).
The concentration of Cu2+ remaining in solution is (3.50×10^-4 - x) M. Using the formation constant expression for the complex ion:
Kf = [Cu(en)22+]/[Cu2+][en]^2
Substituting the given values and the above concentrations at equilibrium,
1.00×10^20 = (1.75×10^-3 - 2x)/[(3.50×10^-4 - x)(1.75×10^-3)^2]
Simplifying and solving for x,
x = 1.29×10^-10 M
Therefore, the concentration of Cu2+ in the solution is 3.50×10^-4 - 1.29×10^-10 M, which is approximately equal to 3.50×10^-4 M.
To know more about concentration, here
brainly.com/question/10725862
#SPJ4
How long will it take a traveling 350m/s to go a distance of 1400m?
Answers
Answer:
6 hours
Explanation:
pls brailiest
Which phrases describe sedimentary rock
Answers
sedimentary rocks are rocks that are combined from other rocks pressed into one.
HELP PLEASE 1pt
Identify the object that has the greatest gravitational pull.
A.
a tennis ball
B.
the moon
C.
the sun
D.
Earth

Answers
The object with the greatest gravitational pull is the Earth (option D).
What is gravitational pull?Gravitational force is a very long-range, but relatively weak fundamental force of attraction that acts between all particles that have mass. It is believed to be mediated by gravitons.
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation states that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with force directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The force of gravitational attraction is directly dependent upon the masses of both objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance that separates their centers.
So as the mass of either object increases, the force of gravitational attraction between them also increases. If the mass of one of the objects is doubled, then the force of gravity between them is doubled. If the mass of one of the objects is tripled, then the force of gravity between them is tripled.
According to this question, Earth has the highest mass among the listed objects, hence, in accordance to the law of universal gravitation, Earth will possess the greatest gravitational pull.
Learn more about gravitational pull at: https://brainly.com/question/13467280
#SPJ1
Help me please
Will give brainliest
Angle I in the picture below is the angle of...
Select one:
a. refraction.
b. inversion.
c. reflection.
d. incidence.
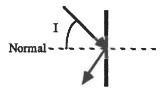
Answers
Angle I in the picture above is the angle of incidence
The angle I and shown can rightly be called the angle of reflection.
According to the laws of reflection, the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie on the same plane. This gives us the idea that when two angles lie on the same plane as the normal, it may be a case of reflection.On the basis of what has been said above, the angle I and shown can rightly be called the angle of reflection.Finally, from the image, we can clearly see that angle I is the angle of reflection.
Learn more about reflection: https://brainly.com/question/12029226
NMR spectroscopy, or ________________________ magnetic resonance spectroscopy, is a very important in the determination of organic structures. This technique relies on the interaction of a particular nucleus with a ________________________ field followed by absorption of energy of a specific ________________________, depending on the chemical environment of the nucleus.
Answers
NMR spectroscopy or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is very important in the determination of the organic structures. This technique relies on the interaction of a particular nucleus with a magnetic field followed by the absorption of energy of a specific frequency, depending on the chemical environment of the nucleus.
NMR spectroscopy is the use of NMR phenomena to study the physical, chemical, and biological properties of matter. Chemists use it to determine the identity and structure of molecules. Physicians use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a multidimensional NMR imaging technique, for diagnostic purposes.
NMR spectroscopy is an analytical chemistry technique used in quality control to determine the content and purity of organic compounds and the molecular structure of compounds. This technique includes nuclear detection.
Learn more about the NMR in
https://brainly.com/question/20111886
#SPJ4
A mothball, composed of naphthalene (C10H8) has a mass of 1.86 g. How many naphthalene molecules does it contain? Express your answer in molecules to three significant figures.
Answers
Answer:
1.476 mol molecules
Explanation:
explain why it is the freezing point depression of a solvent does depend on the concentration of the solute.
Answers
The reason why the freezing point depression of a solvent depends on the concentration, it is because the solute occupies space between the solvent molecules.
The freezing point depression of a solvent depends on the concentration of the soluteThe freezing point depression of a solvent does depend on the concentration of the solute because the solute occupies space between the solvent molecules, thus reducing the number of molecules that can interact.
When a solute is dissolved in a solvent, it takes up space between the solvent molecules. This reduces the number of molecules that can interact, and thus lowers the freezing point of the solvent. The more concentrated the solution, the greater the effect on the freezing point.
Learn more about Solute and Solvent: https://brainly.com/question/25326161
#SPJ4
The equation shows a reaction at equilibrium.
3H2 (g) + N, (8) = 2NH3 (g) + 92 kJ
Which of the following describes what happens if NH is added to the system?
Equilibrium is restored as the reaction shifts toward the reactants
Equilibrium is restored as the reaction shifts toward the products.
Equilibrium is restored as more heat energy is released from the system.
Equilibrium is restored as the concentration is increased to the products
Answers
If NH is introduced to the system, equilibrium is restored as the reaction moves towards the reactants. Option A is correct.
According to Le Chatelier's principle, if a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system will adjust in a way that partially offsets the effect of the stress and restores equilibrium. The reaction:
3H₂ (g) + N₂ (g) ⇌ 2NH₃ (g) + 92 kJ
In this case, adding NH₃ to the system would increase the concentration of products, causing the equilibrium to shift towards the reactants in order to reduce the excess products.
This means that the forward reaction (production of NH₃) would slow down, while the reverse reaction (breakdown of NH₃) would speed up until equilibrium is re-established. Since the forward reaction is exothermic (heat-releasing), increasing the concentration of reactants by shifting the equilibrium towards the left would also decrease the heat energy in the system, helping to partially offset the addition of NH₃. Option A is correct.
To know more about the Equilibrium, here
https://brainly.com/question/30101313
#SPJ1